
If you’ve ever wondered how market prices are determined or how a product’s supply matches its demand, there’s an answer. The laws of supply and demand shape almost every interaction in the consumer market. You might be thinking this isn’t relevant to you as a personal finance connoisseur, but aggregate economics actually affects all of us. When there are shifts or fluctuations in supply and demand, it trickles down to our individual wallets. Everything is interconnected, so understanding how something works at the top can help you make decisions at the bottom. In this article, we’ll explore these laws of supply and demand and understand how they affect the different players in the market.

Table of contents
How do you explain supply and demand?
Supply refers to the ability of the market, or better yet, the producers, to manufacture a good or service. Demand refers to the quantity of commodities consumers are willing and able to buy at a certain price. Supply and demand show the relationship between:
- The number of goods that manufacturers are willing to sell, and
- The quantity consumers are willing to buy at a given price, all things being equal.
Furthermore, the price of a good or service is dependent on the interaction between these two market forces. Now, there’s the law of supply and the law of demand. Let’s look at each of these laws below to get a grasp of the big picture.
Related Reading: Old Age Security Increase in 2023: What You Need to Know
What is the law of supply?
The law of supply states that as the price of a commodity increases, the quantity supplied increases, and vice versa. This simply means that as the price of a good or service increases, producers increase the number of goods produced to maximize profit. Conversely, when the price of a commodity is low, producers may be less willing to supply. This also goes to show there’s a strong correlation between price and quantity. Quantity in supply will vary in response to the change in prices.
What is the law of demand?
The law of demand shows the relationship between the price of goods and the quantity demanded. This law states that as the price of a good increase, the quantity demanded decreases. Conversely, when the price of a good decreases, the quantity demanded increases. The law of demand demonstrates an inverted relationship between price and demand by consumers.
CIBC Investor’s Line Offer
Up to $6.95 per online stock or ETF trade. Plus, there’s no minimum account balance.
What is the equilibrium price?
The equilibrium price is the price point at which demand equals supply. In other words, it’s the moment when the market is in perfect balance. When the quantity of goods demanded is equal to the quantity supplied, the market is said to be in a state of equilibrium. In this state, there is no shortage or surplus of goods or services produced.
The quantity demanded by consumers at the equilibrium price is the same as the quantity supplied by producers. The particular price at which the market reaches its state of equilibrium is referred to as the equilibrium price. At an equilibrium price, buyers can buy exactly the quantity of the product they need. At the same time, sellers can sell the entire quantity they produce while continuing to profit.
Let’s take a look at a practical example of equilibrium price. A shoe company sets the price of its product at $25 per pair and records only 10 sales in the span of 5 months. The shoe company lowers the price of the product to $20 and records 10 sales in just one month. At this price point, the company did not only increase sales, but also made a profit.
From the observed market behavior, if the company further reduces the price of their shoes to $15, demand will become even higher. However, at this price point, the company may record losses instead of profit, negatively impacting the business. But at $20, the supply and demand are in equilibrium. There’s increased demand and the company can meet up with demand without jeopardizing the profit margin. Thus, $20 is the equilibrium price of the product.
Related Reading: Understanding the Various Types of Inflation: A Comprehensive Guide
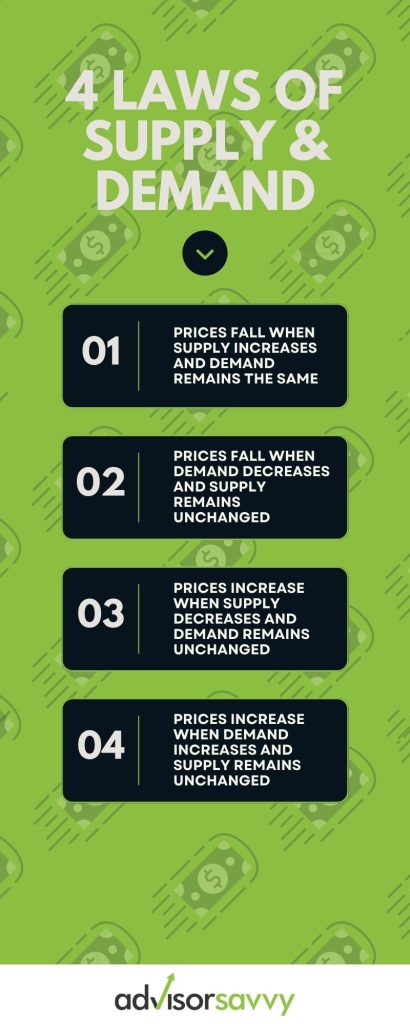
What are the four basic laws of supply and demand?
The law of supply and demand is the bedrock principle of all economic theory. It gives insight into the relationship between demand, supply, and the prices of goods and services. Combining the laws of supply and demand tells you how demand and supply influence a product’s price. Below are the four basic laws of supply and demand.
1. Prices fall when supply increases and demand remains the same
When there’s an increase in supply without a change in demand, the result is often oversupply. In such cases, producers will want to move out the excess stock, and so will beat down prices. The latter is especially true if the product has a short lifespan, such as food or fads. This decrease in prices can boost demand since lower prices incentivize consumers to buy products.
A real life example of this is when a farmer has a particularly good crop yield in a season. They unexpectedly produced more crop than they anticipated. In order to ensure all the crop is utilized and not wasted, the price of the crop is reduced.
2. Prices fall when demand decreases and supply remains unchanged
In a situation where demand continues to decline, there will eventually be a surplus of the product. This market scenario dampens the product’s value, causing a fall in the price of the product.
An excellent instance of this law is fads. Let’s say a new style of fashion is worn by a celebrity. A company decides to mass produce the clothing since many are demanding to wear the same style as the celebrity. But six months later, another celebrity has come out with a more popular fashion style. Consumers will suddenly demand less of the old style. The producer will have to reduce their prices to offload the clothing.
3. Prices increase when supply decreases and demand remains unchanged
When supply decreases and demand remains the same, the result is a shortage of the product. What often follows this market situation is an increase in the price of a product. Usually, customers will pay higher prices for the goods and services they want. This situation is often temporary, and prices return to normal once supply is restored.
A good example of this is the recent COVID-19 pandemic. Supply chain disruptions caused by lockdowns and increased regulation resulted in supply decreases. As a result, the price of certain goods and services increased.
4. Prices increase when demand increases and supply remains unchanged
When demand for a product increases and producers aren’t creating enough to meet increasing demand, a shortage can occur. This will shoot up the price of the product — the shortage of a product causes an increase in its value. However, when supply finally matches the demand level, prices tend to return to normal.

Match to your perfect advisor now.
Getting started is easy, fast and free.
An example of this law is the supply of pumpkins. Throughout the year, demand for pumpkins is pretty stable. But in October for the Halloween season, demand for pumpkins spikes. This causes the price to increase since the supply of pumpkins remains the same. Once November rolls around, everything returns to normal.
Related Reading: Common Law vs Marriage Canada: What are the financial implications?
What is an example of the law of supply and demand?
The truth is, the laws of supply and demand play out in our everyday lives. There are many examples we can discuss, like the few listed above. However, supply and demand are dynamic and influence our decisions everyday. For instance, if you went to the grocery store today to purchase apples, the interaction between supply and demand already influenced the price you paid. Let’s look at a detailed example below.
Let’s say you’re the only person selling rainboots in a town that endures tons of rain. These boots are essential commodities for local dwellers and they cannot get the product anywhere else. As the supplier, you charge your price and the market is in equilibrium.
One day, a local department store adds rainboots to their product offerings. This increases the supply of rainboots in the area. As a result, the original and new supplier must reduce their price because demand for the product is the same, but supply has increased.
Another six months later, a nearby town floods from all the rain and is forced to move to the town. They all lost their rainboots in the flood and need to purchase new ones. Since the demand has increased and supply is the same, the price is driven back upwards.
After the surge of demand for rainboots, the local department store decides to stop selling rainboots because they’re out of stock and don’t wish to continue in the market. The original supplier is able to increase their prices since they’re the only provider of rainboots — back to equilibrium once again.
As you can see, supply and demand is fluid. While the objective is to always have a market in equilibrium, that is rarely the case due to external factors outside of the market’s control. Next time you see a price surge or drop somewhere, try to think of why it might be happening!
Related Reading: What is Inflation?
Why is supply and demand important?
At the end of the day, we all have our budgets to consider. The price of things like food, housing, and entertainment are important because it impacts whether or not we can afford them. By understanding the laws of supply and demand, you can better understand the ebb and flow of prices. It can go both ways too. For instance, estimating when prices will fall so you can wait before buying. Or estimating when prices will rise so you can stock up now. Even though it may seem like supply and demand is way beyond your wallet, the truth is it impacts everyone, even when at large scale!

